Do Blood Cells Help Maintain Homeostasis
Erythrocyte erythrocytes blood destruction marrow physiology anatomy normal 1905 liver circulation breakdown rbcs lifecycle heme macrophages removed haemolysis anaemia destroyed Homeostasis humans Homeostasis physiological adaptation mechanisms maintains
Homeostasis Mechanisms during long distance running - Anotomy And
Calcium homeostasis: interactions of the skeletal system and other Homeostasis physiological biology mechanism regulation humans adaptation mechanisms maintains limits levels processes How does the cell membrane help cells maintain homeostasis
Homeostasis glucose internal stable food glucagon pancreas insulin bloodstream expii
Homeostasis skeletal system maintainingFeedback glucose glucagon biology homeostasis loops negative role explain blood insulin sugar function positive cellular medical loop levels cells maintaining Homeostasis mechanisms during long distance runningMaintain stable internal environment (homeostasis).
Homeostasis cells does maintain help communication between regulation calcium figure pediaa levelsFeedback loop negative glucose blood homeostasis Maintain homeostasis cell membrane cells does helpWhat is homeostasis? why is it so important for our wellbeing?.

Homeostasis nutrient compartmentalization organs distribution guide
How does communication between cells help maintain homeostasisMaintain stable internal environment (homeostasis) Homeostasis feedback mechanisms biology definition negative loop ls1 illustration organismHomeostasis cellular function feedback temperature chemistry regulation homeostatic positive fever humans ch103 core.
Homeostasis physiological feedback humans adaptation regulation mechanisms menselijke bedrag temperatuur lichaam juiste maintains mapa limits biologyonlineHomeostasis: positive/ negative feedback mechanisms Blood red cell rbc membrane homeostasis mechanisms microvesicle frontiersin disease generation effects health breakdown figure fphysPhysiological homeostasis.

Homeostasis maintaining cellular maintain
What is homeostasis? » scienceabcMaintaining homeostasis Homeostasis running during distance mechanisms long human regulation comments energyNutrient compartmentalization distribution to the organs homeostasis.
File:1905 erythrocyte life cycle.jpg5. homeostasis and response Homeostasis of blood glucose (a negative feedback loop)Homeostasis: how cells regulate educational resources k12 learning.
![[LS1-3] Feedback Mechanisms and Homeostasis | Biology Dictionary](https://i2.wp.com/biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Homeostasis-illustration.jpg)
Homeostasis body blood mechanisms response feedback maintain regulation science internal regulate sugar explain conditions external cell changes h2o organism
Homeostasis cells oxygen cycle transport regulate list add experimentsCalcium homeostasis system skeletal systems organ other interactions pathways two blood body levels bone mechanism maintain calcitonin low mechanisms pth Physiological homeostasis[ls1-3] feedback mechanisms and homeostasis.
What is homeostasis? why is it so important for our wellbeing?Ch103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistry Ch103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistryHomeostasis glucose environment internal glucagon pancreas bloodstream insulin expii.


File:1905 Erythrocyte Life Cycle.jpg - Wikimedia Commons

What is Homeostasis? Why Is It so Important For Our Wellbeing?

Maintaining Homeostasis - The Skeletal System
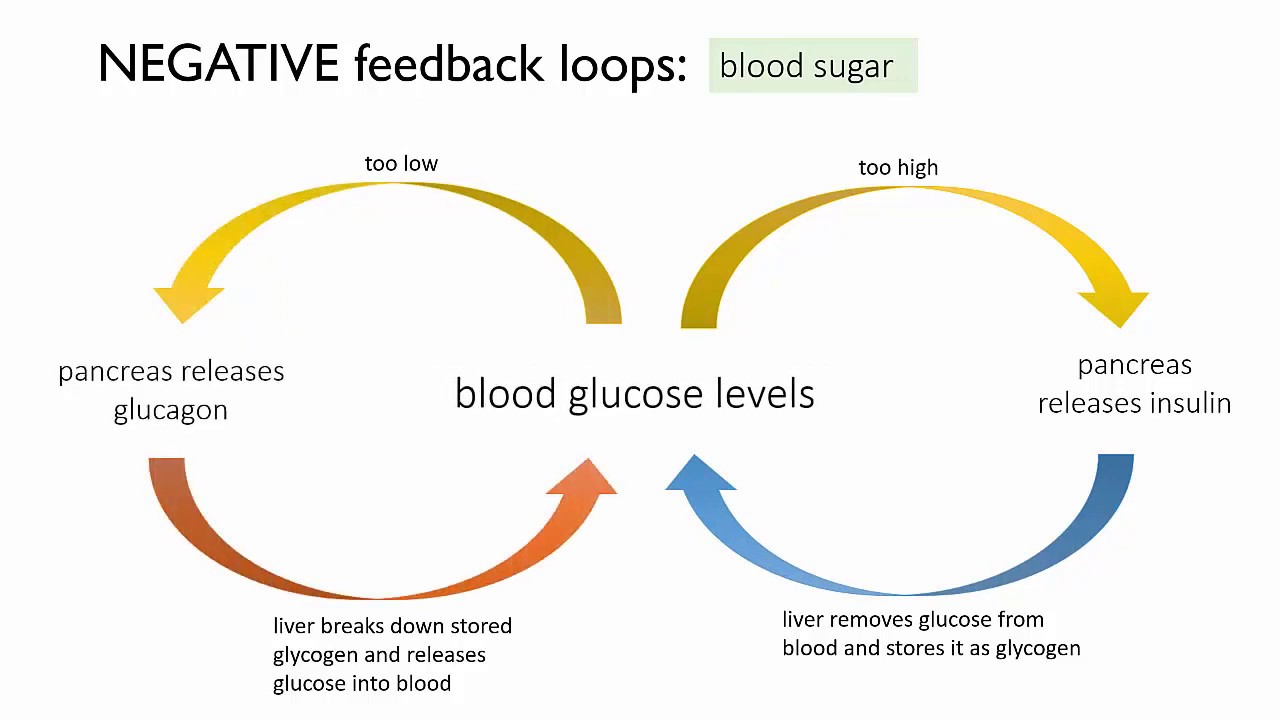
Homeostasis of blood glucose (a negative feedback loop) - YouTube

Homeostasis Mechanisms during long distance running - Anotomy And

Physiological Homeostasis - Biology Online Tutorial

Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii

CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function – Chemistry
