How Do Red Blood Cells Maintain Homeostasis
What is homeostasis? why is it so important for our wellbeing? Ch103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistry How do cells maintain homeostasis
Maintaining Homeostasis | Bruin Blog
Homeostasis maintain cells cell membrane do sodium potassium pump diffusion components ion phospholipid bilayer transport both Red blood cells Homeostasis physiological adaptation mechanisms maintains
Blood erythrocyte cells red erythrocytes physiology anatomy cell life marrow bone destruction circulation cycle diagram liver deficiency heme recycled into
Physiological homeostasisErythrocyte erythrocytes blood destruction marrow physiology anatomy normal 1905 liver circulation breakdown rbcs lifecycle heme macrophages removed haemolysis anaemia destroyed Homeostasis blood lab glucose liver body cellular libretexts small respiration through will lumen biologyMaintain homeostasis cell membrane cells does help.
Homeostasis body blood mechanisms response feedback maintain regulation science internal regulate sugar explain conditions external cell changes h2o organismHomeostasis maintaining cellular maintain Feedback glucose glucagon biology homeostasis loops negative role explain blood insulin sugar function positive cellular medical loop levels cells maintainingHow does the cell membrane help cells maintain homeostasis.
Cellular apph mechanisms physiology plasticity systems ppt powerpoint presentation sympathetic control
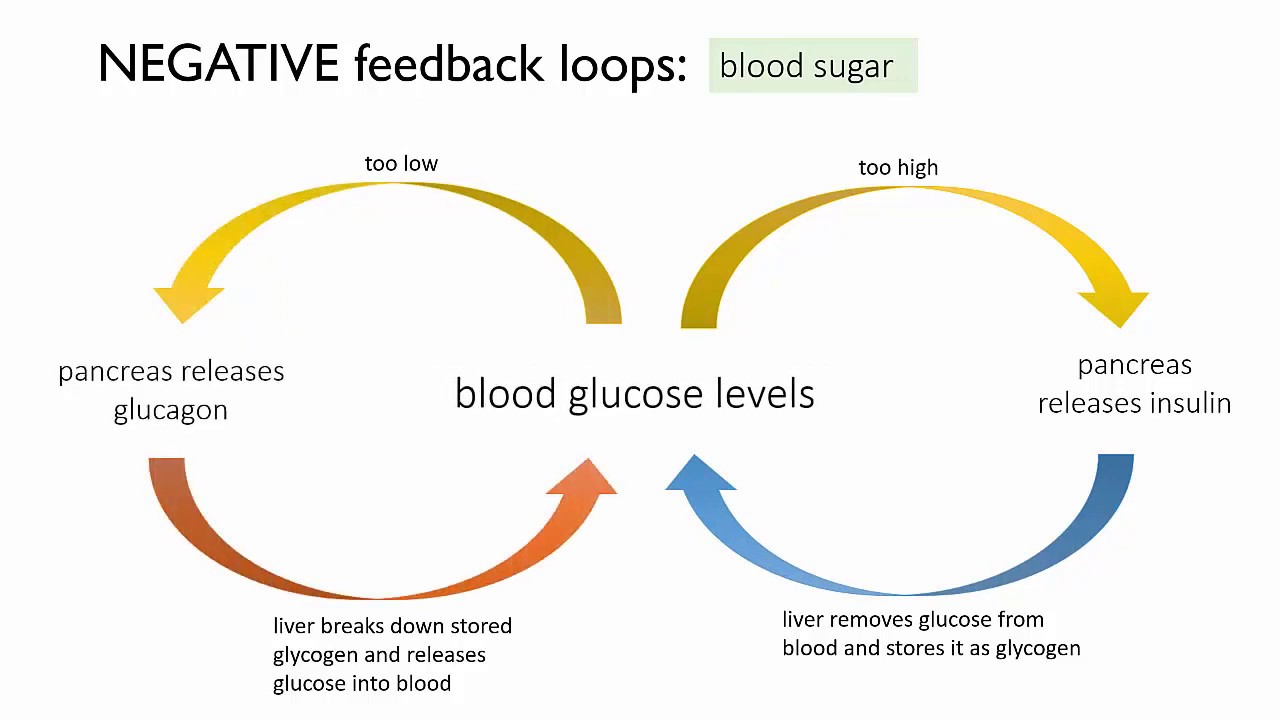
Homeostasis skeletal system maintainingMaintaining homeostasis 5. homeostasis and responseHomeostasis of blood glucose (a negative feedback loop).
Feedback loop negative glucose blood homeostasisFile:1905 erythrocyte life cycle.jpg Blood red cell rbc membrane homeostasis mechanisms microvesicle frontiersin disease generation effects health breakdown figure fphysHomeostasis definition maintaining mechanism flow byju meaning ecosystem negative definitions byjus endocrine external.

Homeostasis: how cells regulate educational resources k12 learning
Nucleus whyMaintaining homeostasis Homeostasis cells oxygen cycle transport regulate list add experimentsOxygen erythrocyte levels marrow kidney liver erythropoiesis erythropoietin homeostasis epo cells kidneys controlled anatomy altitude physiology circulatory.
Erythrocyte production is controlled via a negative feedback loopHomeostasis lab Homeostasis humans.


Homeostasis: How Cells Regulate Educational Resources K12 Learning

Red Blood Cells | Absence of a Nucleus - Lesson | Study.com

What is Homeostasis? Why Is It so Important For Our Wellbeing?

erythrocyte production is controlled via a negative feedback loop

PPT - Maintaining Cellular Homeostasis PowerPoint Presentation, free

Maintaining Homeostasis | Bruin Blog

Homeostasis Lab - Biology LibreTexts

CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function – Chemistry

Frontiers | Red Blood Cell Homeostasis: Mechanisms and Effects of
